VPN vs Proxy: What's the Difference? (2025 Guide)
VPN vs Proxy guide 2025: Compare VPN and proxy servers to choose the right privacy tool. Learn the differences, benefits, and when to use each.
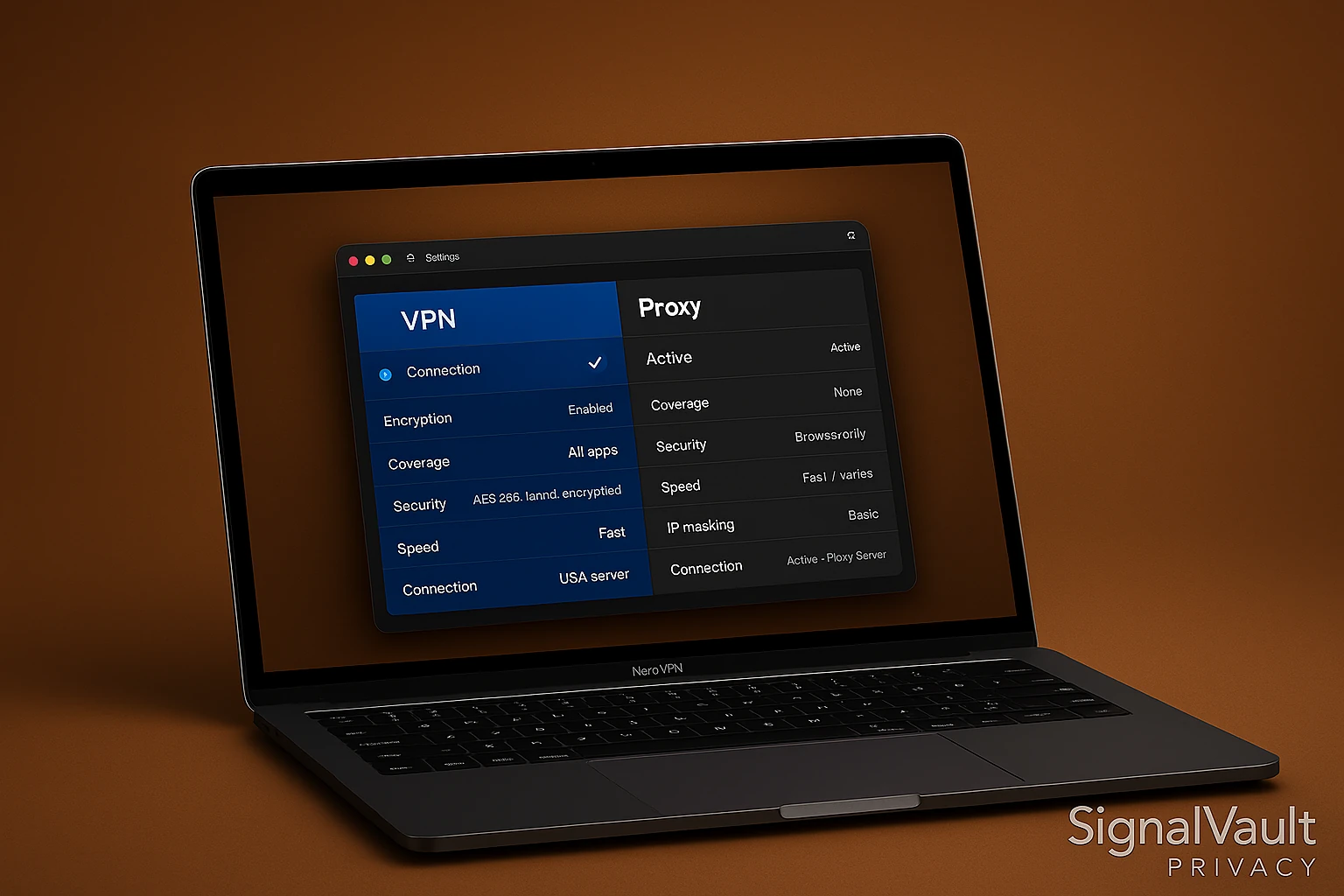
VPNs and proxy servers both hide your IP address, but they work differently. Understanding the differences helps you choose the right privacy tool for your needs. When comparing vpn vs proxy, VPNs provide encryption while proxies only route traffic.
This guide explains VPN vs proxy servers. You’ll learn how they work, their differences, and when to use each. If you’re wondering what is a vpn or how it differs from a proxy, this guide covers everything you need to know.
Quick Comparison: VPN vs Proxy
VPNs encrypt all your internet traffic through a secure tunnel. Proxy servers route traffic through an intermediary server without encryption.
| Feature | VPN | Proxy |
|---|---|---|
| Encryption | Yes, full encryption | No, typically unencrypted |
| Coverage | All apps and websites | Browser or specific apps |
| Security | Strong, protects all traffic | Weak, only hides IP address |
| Speed | Can slow connection slightly | Usually faster |
| Privacy | Strong privacy protection | Basic IP hiding |
| Cost | $2-10/month | Free or low-cost |
Bottom Line: VPNs provide comprehensive security and privacy. Proxy servers only hide your IP address.
What Is a VPN?
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) encrypts all your internet traffic through a secure tunnel. It protects your data from hackers, ISPs, and surveillance.
How VPNs Work
- You connect to a VPN server
- All your traffic goes through an encrypted tunnel
- The VPN server routes your traffic to the internet
- Websites see the VPN server’s IP address, not yours
VPN Benefits
- Encrypts all internet traffic (all apps, not just browser)
- Hides your IP address and location
- Protects data on public Wi-Fi
- Bypasses geo-restrictions and censorship
- Provides strong privacy protection
VPN Limitations
- Can slow your connection slightly (5-15% usually)
- Requires a subscription ($2-10/month typically)
- Some services block VPN IP addresses
Best For: Users who want comprehensive security and privacy for all their internet activities.
Get NordVPN Now → Start protecting all your internet traffic today.
What Is a Proxy Server?
A proxy server routes your internet traffic through an intermediary server. It changes your IP address but doesn’t encrypt your data.
How Proxy Servers Work
- You configure your browser or app to use a proxy
- Your traffic goes through the proxy server
- The proxy forwards your request to the destination
- Websites see the proxy server’s IP address, not yours
Proxy Benefits
- Hides your IP address
- Can be faster than VPNs (no encryption overhead)
- Often free or low-cost
- Easy to set up for specific apps
Proxy Limitations
- Doesn’t encrypt your data
- Only works for configured apps (usually just browser)
- Less privacy protection than VPNs
- Can leak your real IP address
- Free proxies may log your data
Best For: Users who only need to hide their IP address for basic web browsing.
Key Differences: VPN vs Proxy
Here are the main differences between VPNs and proxy servers.
1. Encryption
VPN: Encrypts all your internet traffic with strong encryption (AES-256). This protects your data from hackers, ISPs, and surveillance.
Proxy: Typically doesn’t encrypt your data. Your traffic is visible to anyone monitoring your connection.
Winner: VPN for security and privacy.
2. Coverage
VPN: Protects all apps and websites on your device. Works system-wide, not just in your browser.
Proxy: Usually only works for the configured app (browser or specific application). Doesn’t protect other apps.
Winner: VPN for comprehensive protection.
3. Security
VPN: Provides strong security with encryption, leak protection, and kill switch features.
Proxy: Provides minimal security. Only hides your IP address, doesn’t protect your data.
Winner: VPN for security.
4. Privacy
VPN: Strong privacy protection with no-logs policies and encrypted connections.
Proxy: Basic privacy (IP hiding only). Free proxies may log your data.
Winner: VPN for privacy.
5. Speed
VPN: Can slow your connection slightly (5-15% usually) due to encryption overhead.
Proxy: Usually faster since there’s no encryption. May be faster than direct connection in some cases.
Winner: Proxy for raw speed (but VPN speed is usually acceptable).
6. Cost
VPN: Requires a subscription ($2-10/month typically). Free VPNs exist but have limitations.
Proxy: Often free or low-cost. Premium proxies available for more features.
Winner: Proxy for cost (but VPN value is better overall).
7. Setup
VPN: Easy setup with dedicated apps. Install app, connect, done.
Proxy: Requires manual configuration in browser or app settings. More technical.
Winner: VPN for ease of use.
8. Reliability
VPN: Reliable connections with automatic reconnection and kill switch features.
Proxy: Can disconnect frequently. No automatic reconnection.
Winner: VPN for reliability.
When to Use a VPN
Use a VPN when you need comprehensive security and privacy.
Use VPNs For:
- Protecting all your internet traffic (all apps, not just browser)
- Securing public Wi-Fi connections
- Bypassing geo-restrictions and censorship
- Strong privacy protection
- Encrypting sensitive data (banking, email)
- Torrenting and P2P file sharing
- Accessing blocked websites
Best VPN Services
- NordVPN: Best overall ($3.39/month)
- Surfshark: Best budget option ($2.49/month)
- ProtonVPN: Best privacy-focused option (free tier available)
Get NordVPN Now → Start protecting all your internet traffic.
When to Use a Proxy
Use a proxy when you only need basic IP hiding for web browsing.
Use Proxies For:
- Hiding IP address for basic web browsing
- Accessing geo-blocked websites (when speed matters more than security)
- Quick, temporary IP changes
- Free options for minimal needs
- Specific app configuration (when VPN isn’t needed)
Best Proxy Services
- Bright Data: Premium proxy service (paid)
- Smartproxy: Residential proxies (paid)
- Free proxy lists: Available online but less reliable
Note: Free proxies often log your data and may be slower. Use with caution.
VPN vs Proxy: Which Should You Choose?
Choose based on your needs.
Choose a VPN If:
- You want comprehensive security and privacy
- You use public Wi-Fi regularly
- You need protection for all apps (not just browser)
- You want strong encryption for sensitive data
- You need reliable, long-term privacy protection
Recommended: NordVPN for most users, Surfshark for budget-conscious users.
Choose a Proxy If:
- You only need basic IP hiding for web browsing
- Speed is more important than security
- You only need temporary, occasional use
- You want a free option for minimal needs
- You’re configuring specific applications
Note: For most users, a VPN provides better value and protection.
Can You Use Both VPN and Proxy?
Yes, you can use both, but it’s usually unnecessary and can slow your connection.
When to Use Both
- Advanced privacy needs (Tor + VPN)
- Specific routing requirements
- Testing and debugging
Why Usually Unnecessary
- VPNs already provide proxy functionality (IP hiding)
- Using both adds complexity and slows connection
- VPN alone is sufficient for most users
Bottom Line: Choose one based on your needs. VPN for comprehensive protection, proxy for basic IP hiding.
Common VPN vs Proxy Questions
Is a VPN better than a proxy? Yes, for most users. VPNs provide encryption, comprehensive protection, and better privacy. Proxies only hide your IP address.
Can I use a proxy instead of a VPN? Yes, but you’ll lose encryption and comprehensive protection. Only use a proxy if you only need basic IP hiding.
Do I need both VPN and proxy? No, usually not. VPNs already provide proxy functionality (IP hiding) plus encryption. Using both is usually unnecessary.
Are free proxies safe? Free proxies are often less safe. They may log your data, inject ads, or be slower. Use paid services when possible.
Which is faster: VPN or proxy? Proxies are usually faster since there’s no encryption overhead. But modern VPNs are fast enough for most users (5-15% slower typically).
Can I use a VPN for streaming? Yes, VPNs work well for streaming. Many VPNs (NordVPN, Surfshark) unblock streaming services reliably.
Can I use a proxy for streaming? Some proxies work for streaming, but they’re less reliable. VPNs are better for consistent streaming access.
Conclusion
VPNs and proxy servers both hide your IP address, but VPNs provide comprehensive security and privacy protection.
For Most Users: Choose a VPN for comprehensive protection.
For Basic Needs: Use a proxy only if you only need IP hiding for web browsing.
Recommendation: Get NordVPN Now → Start protecting all your internet traffic today.
Related Guides
FAQs
What’s the difference between VPN and proxy? VPNs encrypt all your internet traffic and protect all apps. Proxies only hide your IP address and typically only work for configured apps (usually browser).
Is a VPN the same as a proxy? No. VPNs encrypt all your traffic and protect all apps. Proxies only hide your IP address and don’t encrypt your data.
Should I use a VPN or proxy? For most users, use a VPN for comprehensive security and privacy. Use a proxy only if you only need basic IP hiding for web browsing.
Can I use both VPN and proxy together? Yes, but it’s usually unnecessary and can slow your connection. VPNs already provide proxy functionality plus encryption.
Are free proxies safe to use? Free proxies are often less safe. They may log your data, inject ads, or be slower. Use paid services when possible.